Kicking off with The Role of Servers in Edge Computing, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone inspirational with positive tone style that unfolds with each word.
Edge computing has revolutionized the way data is processed and delivered, with servers playing a crucial role in this dynamic environment. As we delve deeper into the significance of servers in edge computing, we uncover a world of possibilities where performance and security are paramount.
The Basics of Edge Computing
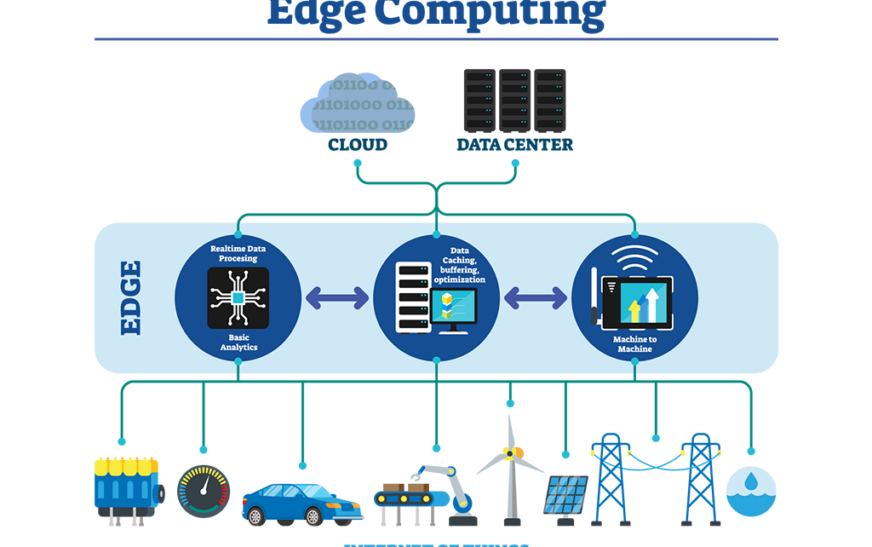
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, rather than relying on a centralized data center. This approach helps reduce latency and improves the overall performance of applications, making it ideal for use cases that require real-time data processing and analysis.
Examples of Edge Computing Applications
- Smart Cities: Edge computing is used in smart city applications to collect and process data from various sensors and devices in real-time. This enables efficient traffic management, waste management, and energy optimization.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing plays a crucial role in autonomous vehicles by processing data from sensors quickly to make split-second decisions, ensuring the safety of passengers and pedestrians.
- Industrial IoT: In industrial settings, edge computing is used to monitor equipment, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes by analyzing data at the edge of the network.
Introduction to Servers in Edge Computing: The Role Of Servers In Edge Computing
In edge computing, servers play a crucial role in processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving overall performance compared to traditional data center servers.
Role of Servers in Edge Computing
Servers in edge computing environments perform key functions that enable efficient data processing and storage at the edge of the network:
- 1. Real-time data processing:Servers at the edge are responsible for processing data quickly and efficiently, allowing for real-time decision-making and analysis.
- 2. Low-latency communication:By handling data processing closer to the source, servers in edge computing reduce latency in communication between devices and the network.
- 3. Distributed computing:Edge servers enable distributed computing by spreading computational tasks across multiple servers, optimizing resource utilization.
- 4. Data filtering and aggregation:Servers at the edge filter and aggregate data before sending it to the central data center, reducing the amount of data transmitted and improving network efficiency.
Types of Servers Used in Edge Computing
When it comes to edge computing, different types of servers are commonly deployed to handle the processing and storage needs of edge devices. These servers play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable operations at the edge of the network.
Centralized Servers
Centralized servers in edge computing setups are typically located in a central data center or cloud environment. These servers are powerful in terms of processing capabilities and storage capacity, making them ideal for handling complex tasks and large amounts of data.
Setting up a proxy server can offer numerous benefits in terms of security and privacy. Discover the step-by-step process for creating your own proxy server with the help of this detailed guide on How to Set Up a Proxy Server and take control of your online activities.
However, they may introduce latency issues due to the distance between the central server and edge devices.
Securing server APIs is crucial in protecting sensitive data and preventing cyber attacks. By following the best practices outlined in this comprehensive guide on How to Secure Server APIs , you can ensure the safety and integrity of your server communications.
Micro Servers
Micro servers are compact, energy-efficient servers that are well-suited for edge computing environments. These servers are designed to be lightweight and low-power, making them perfect for deployment in remote locations or edge devices with limited space and resources. Micro servers are highly scalable and can be easily deployed in large numbers to support distributed edge computing architectures.
Edge Servers
Edge servers are specifically designed to be deployed at the edge of the network, closer to where data is generated and consumed. These servers are optimized for low-latency processing and real-time data analytics, making them essential for applications that require immediate responses and decision-making capabilities.
Digital tools play a vital role in boosting conversion rates for businesses. Learn how to leverage the power of these tools to enhance your online presence and drive more sales by checking out this insightful article on How Digital Tools Can Improve Your Conversion Rates.
Edge servers are capable of handling a variety of workloads, from IoT devices to industrial sensors, in a decentralized manner.
Virtualized Servers
Virtualized servers in edge computing environments leverage virtualization technology to create multiple virtual instances on a single physical server. This allows for better resource utilization and flexibility in managing workloads across different edge devices. Virtualized servers enable efficient resource allocation and dynamic scaling based on the demands of edge applications, improving overall performance and scalability.
Server Management and Orchestration in Edge Computing

Managing servers in distributed edge environments poses several challenges due to the unique nature of edge computing. The decentralized nature of edge networks, with servers distributed across various locations, makes it difficult to ensure consistent performance and resource utilization.
Challenges of Server Management in Edge Computing, The Role of Servers in Edge Computing
- Latency: With servers located closer to end-users, latency becomes a critical factor in edge computing. Managing servers to minimize latency and ensure fast response times can be challenging.
- Scalability: The dynamic nature of edge environments requires the ability to scale servers up or down based on demand. Managing this scalability efficiently is crucial for optimal performance.
- Security: Securing servers distributed across different edge locations from potential cyber threats and unauthorized access presents a significant challenge in server management.
Role of Orchestration Tools in Server Management
Orchestration tools play a vital role in optimizing server performance and resource utilization in edge computing environments. These tools help in automating the deployment, configuration, and management of servers, ensuring efficient operations.
- Resource Allocation: Orchestration tools help in allocating resources effectively across distributed servers based on workload requirements, optimizing resource utilization.
- Load Balancing: By distributing workloads evenly across servers, orchestration tools help in balancing the load and preventing server overload, ensuring consistent performance.
- Automated Scaling: Orchestration tools enable automated scaling of servers based on demand, ensuring that resources are dynamically adjusted to meet fluctuating workloads.
Security Considerations for Servers in Edge Computing
When it comes to edge computing, the security landscape is significantly different from traditional data centers. Servers at the edge face unique security risks that require specific attention to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Physical Security Measures
- Implementing physical security measures such as access controls, surveillance cameras, and environmental monitoring at edge locations can help prevent unauthorized access to servers.
- Utilizing secure enclosures and cabinets to protect servers from tampering or theft in remote edge environments is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data.
Network Security Protocols
- Enforcing strong network security protocols, including encryption, VPNs, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, can help secure data transmission between edge servers and the central cloud.
- Regularly updating and patching network security software to address vulnerabilities and protect against cyber threats is essential for maintaining a secure edge computing environment.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
- Implementing end-to-end data encryption and access controls to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive information stored on edge servers can help prevent data breaches and unauthorized data manipulation.
- Leveraging multi-factor authentication and role-based access controls can enhance data security and ensure that only authorized personnel can access critical systems and applications at the edge.
Security Monitoring and Incident Response
- Deploying security monitoring tools and establishing incident response protocols to detect and respond to security breaches or anomalies in real-time is crucial for proactively addressing security threats at the edge.
- Conducting regular security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments to identify and remediate security gaps in edge server infrastructure can help strengthen overall security posture.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, servers are the backbone of edge computing, driving innovation and efficiency in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. By understanding their role and implementing best practices, we can harness the full potential of edge computing while ensuring optimal performance and security.