With The Role of Servers in Cloud Computing at the forefront, embark on a journey exploring the essential role servers play in enabling cloud services with innovation and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide delves into the different types of servers, server management best practices, scalability, security considerations, and much more.
Introduction to Servers in Cloud Computing
In the world of cloud computing, servers play a fundamental role in enabling the delivery of various services over the internet. These servers act as the backbone of the cloud infrastructure, providing the necessary computing power, storage capacity, and networking capabilities to support a wide range of applications and workloads.Servers in cloud computing are responsible for processing and storing data, running applications, and managing virtual resources.
They act as the central hub that connects users to the cloud environment, allowing them to access and interact with the services offered by cloud providers.
Looking to boost your social media presence? Discover The Best Digital Tools for Social Media Growth and watch your followers and engagement skyrocket!
Popular Server Types in Cloud Environments
- Virtual Private Servers (VPS): VPS servers provide users with dedicated resources within a shared physical server, offering a cost-effective solution for hosting websites and applications.
- Public Cloud Servers: These servers are hosted by cloud providers and are accessible to multiple users over the internet. They offer scalability and flexibility for businesses looking to expand their operations.
- Dedicated Servers: Dedicated servers are physical servers that are exclusively used by a single organization. They provide enhanced performance and security for applications that require high levels of computing power.
Types of Servers in Cloud Computing
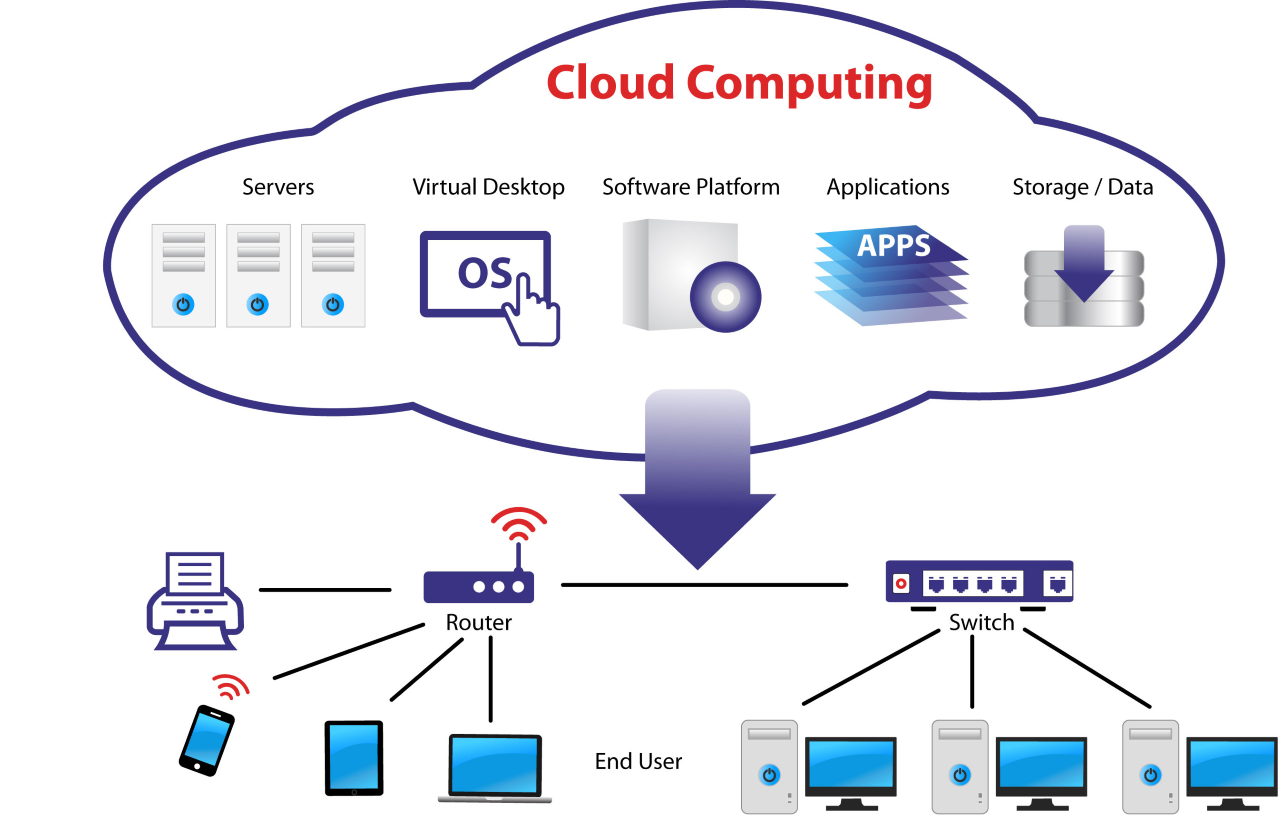
There are different types of servers commonly used in cloud computing, each serving specific functions and purposes. Let’s explore the main server types and compare physical servers with virtual servers in the cloud.
1. Physical Servers
Physical servers are tangible hardware devices that are installed and maintained on-premises or in data centers. These servers handle various tasks and processes within the cloud infrastructure.
- Provide dedicated resources to specific applications or services.
- Require physical space, cooling systems, and power supply for operation.
- Offer high performance and reliability for demanding workloads.
2. Virtual Servers
Virtual servers are software-based instances created on a physical server, allowing for multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine. These servers offer scalability and flexibility in the cloud environment.
- Enable efficient resource allocation and utilization through virtualization technology.
- Can be easily provisioned, scaled up or down based on demand, and migrated across different physical servers.
- Reduce costs by optimizing hardware usage and maximizing server efficiency.
3. Comparison
Physical Servers vs. Virtual Servers
| Physical Servers | Virtual Servers |
|---|---|
| Require dedicated hardware and maintenance. | Share physical resources and can be easily replicated. |
| Provide high performance for specific workloads. | Offer scalability and flexibility for dynamic workloads. |
| Have higher upfront costs and long-term maintenance expenses. | Reduce costs through efficient resource allocation and utilization. |
Server Management in Cloud Computing
Effective server management in a cloud environment is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. By efficiently managing servers, cloud providers can meet the demands of their users while maximizing resource utilization and minimizing downtime.
Creating a strong brand identity is crucial, and with the help of digital tools, it becomes easier. Explore how Digital Tools Can Help You Create a Cohesive Brand Identity to stand out in the crowded market.
Role of Automation Tools, The Role of Servers in Cloud Computing
Automation tools play a vital role in managing servers in the cloud by streamlining and automating routine tasks such as provisioning, monitoring, and scaling. These tools help reduce manual intervention, improve efficiency, and enhance overall system reliability. By automating server management processes, organizations can respond faster to changing demands and ensure consistent performance across their cloud infrastructure.
Best Practices for Optimization
- Implement proactive monitoring: Utilize monitoring tools to track server performance metrics and identify potential issues before they impact operations.
- Optimize resource allocation: Ensure resources are allocated efficiently to meet workload demands without overprovisioning, which can lead to unnecessary costs.
- Implement scalability strategies: Utilize auto-scaling capabilities to dynamically adjust server capacity based on workload fluctuations, ensuring optimal performance during peak times.
- Regularly update and patch servers: Keep servers up to date with the latest security patches and software updates to enhance system security and stability.
- Implement security best practices: Utilize encryption, access controls, and other security measures to protect server data and prevent unauthorized access.
Scalability and Elasticity of Servers in Cloud Computing
In cloud computing, the scalability and elasticity of servers play a crucial role in meeting the dynamic demands of users and applications. Scalability refers to the ability of servers to handle an increasing workload by adding resources, while elasticity focuses on the flexibility to adjust resources based on demand.
Scalability of Servers in Cloud Computing
Scalability is essential in cloud computing to ensure that services can accommodate growing user bases and workload without compromising performance. Servers can be scaled vertically by adding more resources to a single server or horizontally by adding more servers to distribute the workload.
- Vertical Scaling: This involves increasing the resources, such as CPU, memory, or storage, of a single server to handle additional load. It is suitable for applications that require more power rather than distribution.
- Horizontal Scaling: This method involves adding more servers to the existing infrastructure to distribute the load. It allows for better resource utilization and improved fault tolerance.
Elasticity of Servers in Cloud Computing
Server elasticity enables cloud services to adapt to fluctuating demand in real-time, ensuring optimal resource utilization and cost-effectiveness. It allows for automatic scaling up or down of servers based on workload requirements.
“Server elasticity ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, reducing costs and improving overall performance in a dynamic environment.”
Embracing the digital era means utilizing the Top Digital Tools for Content Repurposing to maximize your reach and engagement. Repurpose your content effortlessly and watch your audience grow!
- Auto-Scaling: Cloud platforms can be configured to automatically adjust the number of servers based on predefined metrics, such as CPU utilization or incoming traffic. This helps in maintaining performance during peak times and cutting costs during low demand periods.
- On-Demand Scaling: Users can manually adjust server resources based on immediate needs, allowing for quick responses to sudden spikes in traffic or workload. This flexibility ensures that resources are used optimally at all times.
Security Considerations for Servers in Cloud Computing: The Role Of Servers In Cloud Computing
When it comes to servers in cloud computing, security is a top priority. The decentralized nature of cloud servers brings about unique challenges that need to be addressed to protect sensitive data and ensure smooth operations.
Securing Cloud Servers
- Implement strong access controls: Limiting access to cloud servers to only authorized personnel is crucial in preventing unauthorized users from compromising data or resources.
- Regularly update security patches: Keeping server software up to date with the latest security patches helps in closing vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cyber attackers.
- Use encryption for data protection: Encrypting data stored on cloud servers adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for malicious actors to access sensitive information.
- Monitor server activity: Continuous monitoring of server activity allows for the early detection of any suspicious behavior, helping in identifying and mitigating security threats in a timely manner.
Importance of Data Encryption and Access Control
One of the most critical aspects of securing servers in the cloud is data encryption and access control. By encrypting data at rest and in transit, organizations can safeguard their information from unauthorized access. Additionally, implementing robust access controls ensures that only authorized users can interact with cloud servers, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized modifications.
As we conclude this insightful discussion on The Role of Servers in Cloud Computing, remember the crucial role servers play in the backbone of cloud services, ensuring optimal performance and security for businesses and individuals alike.