The Role of Servers in Big Data Management sets the stage for understanding the pivotal role servers play in handling and processing vast amounts of data, shaping the landscape of efficient data management.
From the importance of server configurations to security considerations, this topic delves into the core aspects that drive effective big data management strategies.
Importance of Servers in Big Data Management
When it comes to managing big data effectively, servers play a crucial role in handling the massive volumes of information involved. These powerful machines are essential for storing, retrieving, and analyzing data efficiently, ensuring that businesses can make informed decisions based on valuable insights.
Efficient Data Processing
Servers are the backbone of big data management, as they are responsible for processing and organizing the vast amounts of information generated daily. Their high computational power and storage capacity enable them to handle complex algorithms and queries, allowing for quick data retrieval and analysis.
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the key advantages of servers in big data management is their scalability and flexibility. Businesses can easily scale their server infrastructure to accommodate growing data volumes, ensuring that they can adapt to changing needs and requirements without compromising performance.
Impact on Decision-Making
The performance of servers directly impacts the overall big data management strategy of an organization. Slow or inefficient servers can lead to delays in data processing, affecting the timeliness and accuracy of insights generated. On the other hand, high-performance servers enable real-time analytics and decision-making, giving businesses a competitive edge in today’s data-driven environment.
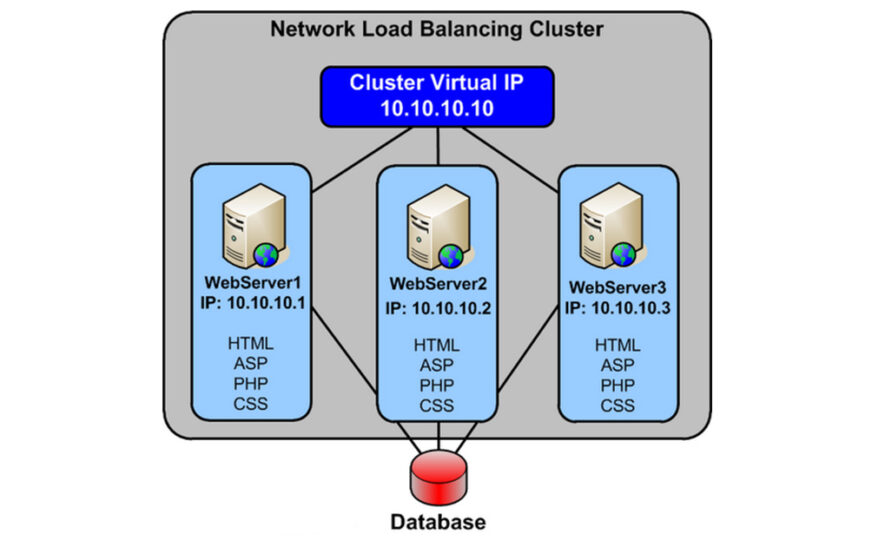
Types of Servers Used in Big Data Management
When it comes to managing big data, various types of servers play a crucial role in processing and storing massive amounts of information efficiently. Let’s explore the different types of servers commonly used in big data environments.
Utilizing the right tools is crucial for effective content distribution in the digital world. Explore the Top Digital Tools for Content Distribution to maximize your reach and engagement with your target audience.
Traditional Servers, The Role of Servers in Big Data Management
Traditional servers refer to physical servers that are located on-premises within an organization’s data center. These servers are dedicated to specific tasks and are often used for processing structured data in a traditional relational database management system (RDBMS) environment. Traditional servers have been the norm for many years and offer a high level of control and security over data.
Cloud-Based Servers
Cloud-based servers, on the other hand, are virtual servers that are hosted in the cloud by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. These servers offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, as organizations can easily scale up or down based on their big data processing needs.
Enhancing your influencer outreach strategy is key to boosting brand awareness. Discover how Digital Tools Can Enhance Your Influencer Outreach and help you build strong relationships with influencers to amplify your message.
Cloud-based servers are ideal for handling unstructured data and can provide on-demand resources for processing large datasets.
Market research is essential for understanding consumer behavior and trends. Stay ahead of the competition by utilizing The Best Digital Tools for Market Research to gather valuable insights and make informed business decisions.
Comparison of Characteristics
- Traditional servers are physical machines, while cloud-based servers are virtual instances hosted in the cloud.
- Traditional servers require a significant upfront investment in hardware and maintenance, whereas cloud-based servers operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing for cost savings.
- Cloud-based servers offer scalability, allowing organizations to quickly expand or reduce their computing resources based on demand, while traditional servers may require hardware upgrades to accommodate growth.
- Traditional servers provide greater control and security over data, as organizations have full ownership of the hardware, whereas cloud-based servers rely on the security measures implemented by the cloud provider.
Scalability and Flexibility
When it comes to adapting to changing big data requirements, servers play a critical role in ensuring scalability and flexibility. Cloud-based servers excel in this aspect, as organizations can easily adjust their computing resources to accommodate fluctuations in data volume and processing needs.
Traditional servers, while reliable and secure, may require more time and investment to scale up or down, making them less flexible in dynamic big data environments.
Server Configuration for Optimal Big Data Performance: The Role Of Servers In Big Data Management
In order to achieve optimal performance in managing big data workloads, it is crucial to properly configure servers. This involves setting up hardware specifications and tuning server settings to enhance efficiency and speed in handling big data tasks.
Importance of Hardware Specifications
When configuring servers for big data processing, hardware specifications play a key role in determining performance. Here are some important considerations:
- CPU:The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is responsible for executing instructions and processing data. Choosing a high-performance CPU with multiple cores can significantly improve processing speed for handling big data workloads.
- RAM:Random Access Memory (RAM) is crucial for storing and accessing data quickly. More RAM allows for faster data processing and analysis, especially when dealing with large datasets in big data management.
- Storage Capacity:Adequate storage capacity is essential for storing large volumes of data. Opt for high-capacity storage solutions such as Solid State Drives (SSDs) or Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) to ensure efficient data storage and retrieval.
Best Practices for Server Settings
To optimize server performance for big data management, consider implementing the following best practices:
- Optimize Network Configuration:Ensure high-speed network connectivity to facilitate data transfer between servers and storage systems, reducing latency and improving overall performance.
- Utilize Parallel Processing:Implement parallel processing techniques to distribute workloads across multiple CPU cores, enabling faster data processing and analysis.
- Monitor Server Performance:Regularly monitor server performance metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O to identify bottlenecks and optimize server settings for improved efficiency.
- Implement Data Compression:Use data compression techniques to reduce the size of data stored on servers, minimizing storage space requirements and improving data transfer speeds.
Security Considerations for Servers in Big Data Environments
Securing servers in big data management is paramount to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access to valuable data. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to maintain data integrity and confidentiality in big data setups.
Access Controls and Encryption
One of the key strategies for enhancing security in big data environments is the implementation of access controls and encryption. Access controls help restrict unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data, while encryption ensures that data is protected even if it falls into the wrong hands.
Data Integrity and Confidentiality
Challenges related to maintaining data integrity and confidentiality on servers in big data environments include ensuring that data is not tampered with or accessed by unauthorized individuals. Implementing secure protocols and encryption techniques can help mitigate these risks and protect the integrity of the data.
In conclusion, the discussion on The Role of Servers in Big Data Management emphasizes the critical functions servers perform in optimizing data processing and safeguarding sensitive information, paving the way for a more secure and efficient data management ecosystem.