Embark on a journey through The Best Practices for Server Decommissioning, where data security and legal implications take center stage, guiding you towards a thorough understanding of this critical process.
Explore the steps involved in planning, data backup, server deactivation, and hardware disposal to ensure a seamless and secure decommissioning process.
Importance of Server Decommissioning
Proper server decommissioning is crucial for maintaining data security. When servers are no longer in use, they still contain sensitive information that can be vulnerable to security breaches if not decommissioned correctly. It is essential to follow best practices to ensure that data is securely wiped and the server hardware is disposed of properly.
Data Security Risks
Improper decommissioning of servers can lead to significant risks for organizations. If data is not securely wiped from the server before disposal, it can be accessed by unauthorized individuals, leading to data breaches and potential exposure of confidential information. This can have severe consequences for businesses, including financial losses and damage to their reputation.
Implementing the best practices for server patch management is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient IT infrastructure. Regular updates and patches help prevent cybersecurity threats and ensure system reliability. Discover more about The Best Practices for Server Patch Management to safeguard your server environment.
Legal Implications
Failure to follow best practices for server decommissioning can also result in legal implications for organizations. Depending on the industry and location, there may be specific regulations governing the proper disposal of electronic devices and data security measures. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to fines, legal action, and other penalties.
Utilizing digital tools is essential for tracking and analyzing website traffic. By employing tools like Google Analytics and SEMrush, businesses can gain valuable insights to optimize their online presence effectively. Learn more about Using Digital Tools to Track and Analyze Website Traffic to stay ahead of the competition.
It is essential for organizations to adhere to the relevant laws and guidelines to avoid legal consequences.
Planning Phase
When it comes to server decommissioning, the planning phase is crucial to ensure a smooth and successful process. This phase involves detailed steps and the involvement of key stakeholders to create a comprehensive decommissioning plan.
Creating engaging landing pages is vital for capturing leads and driving conversions. With the help of top digital tools like Unbounce and Leadpages, businesses can design high-converting landing pages with ease. Explore the Top Digital Tools for Creating Landing Pages to enhance your digital marketing efforts.
Steps in Planning a Server Decommissioning Process
- Assess the current server infrastructure: Identify the servers that need to be decommissioned, their roles, and dependencies.
- Define the decommissioning goals: Determine the reasons for decommissioning each server and set clear objectives for the process.
- Inventory hardware and software: Create a detailed inventory of all hardware components and software applications running on the servers to be decommissioned.
- Plan data migration or archival: Develop a strategy for migrating critical data to new servers or archiving data that is no longer needed.
- Establish a timeline: Set a timeline for the decommissioning process, including key milestones and deadlines for completion.
- Allocate resources: Ensure that the necessary resources, such as IT staff, equipment, and tools, are available to support the decommissioning activities.
Key Stakeholders in the Planning Phase
- IT Department: IT professionals who will be responsible for carrying out the decommissioning process.
- Business Owners: Stakeholders who can provide insights into the impact of server decommissioning on business operations.
- Compliance Officers: Individuals who can ensure that decommissioning activities comply with regulatory requirements and data protection laws.
- Data Owners: Individuals responsible for managing and safeguarding the data stored on the servers being decommissioned.
Importance of Creating a Detailed Decommissioning Plan
Creating a detailed decommissioning plan is essential to ensure that the process is well-organized, efficient, and minimizes risks. A comprehensive plan helps in:
Avoiding disruptions to business operations.
– Ensuring the secure disposal of hardware and data. – Mitigating potential security risks and data breaches. – Facilitating the transition to new server infrastructure smoothly.
Data Backup and Migration

When decommissioning a server, it is crucial to prioritize data backup and migration to ensure the security and integrity of valuable information.
Importance of Data Backup
- Backing up data before decommissioning a server helps prevent data loss and ensures that important information is not permanently deleted.
- It provides a safety net in case of any unexpected issues during the decommissioning process, allowing for easy restoration of data if needed.
- By having a backup, organizations can maintain compliance with data protection regulations and safeguard sensitive information.
Best Practices for Secure Data Migration
- Encrypt data during the migration process to protect it from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Use secure transfer methods such as secure FTP or VPNs to ensure data is transmitted safely to new servers or storage systems.
- Implement access controls and authentication mechanisms to restrict access to migrated data only to authorized personnel.
Verifying Data Backup Completeness and Integrity
- Conduct regular tests and checks on data backups to ensure they are complete and up-to-date.
- Verify the integrity of data backups by comparing checksums or running validation checks to detect any errors or corruption.
- Document the verification process and results to maintain a record of data backup integrity for future reference.
Server Deactivation
When it comes to server decommissioning, deactivating a server is a crucial step to prevent unauthorized access and ensure a smooth transition out of production environments. Properly documenting these activities is key to maintaining security and organization throughout the process.
Steps for Server Deactivation
- Disable user access and permissions to the server to prevent any unauthorized logins or data breaches.
- Remove the server from any load balancers or DNS configurations to ensure it is no longer in use for production traffic.
- Shut down the server and disconnect any physical connections to isolate it from the network.
Removing the Server from Production Environments
- Notify stakeholders and relevant teams about the server deactivation to avoid any disruptions or confusion.
- Update documentation and asset registers to reflect the removal of the server from production environments.
- Perform a final check to ensure all dependencies on the server have been addressed before proceeding with removal.
Best Practices for Documenting Server Deactivation Activities, The Best Practices for Server Decommissioning
- Keep a detailed log of all steps taken during the deactivation process, including dates, times, and individuals involved.
- Document any issues or challenges encountered during server deactivation and how they were resolved.
- Archive all relevant information and documentation for future reference or audits.
Hardware Disposal
When it comes to server decommissioning, proper disposal of hardware is a critical step in ensuring security and environmental responsibility. In this section, we will delve into environmentally friendly methods for disposing of decommissioned hardware, the importance of securely wiping data from such hardware, and relevant regulations and standards that govern hardware disposal.
Environmentally Friendly Disposal Methods
- Recycling: Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to responsibly recycle hardware components.
- Donation: Consider donating decommissioned hardware to organizations or schools in need.
- Repurposing: Explore options to repurpose hardware for internal use or as backup systems.
Secure Data Wiping
Before disposing of hardware, it is crucial to securely wipe all data to prevent any sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. Utilize data wiping software or physical destruction methods to ensure data is irretrievable.
Regulations and Standards
It is essential to comply with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection laws when disposing of hardware to avoid legal repercussions.
Adhere to standards like NIST SP 800-88 for media sanitation to maintain data security during hardware disposal processes.
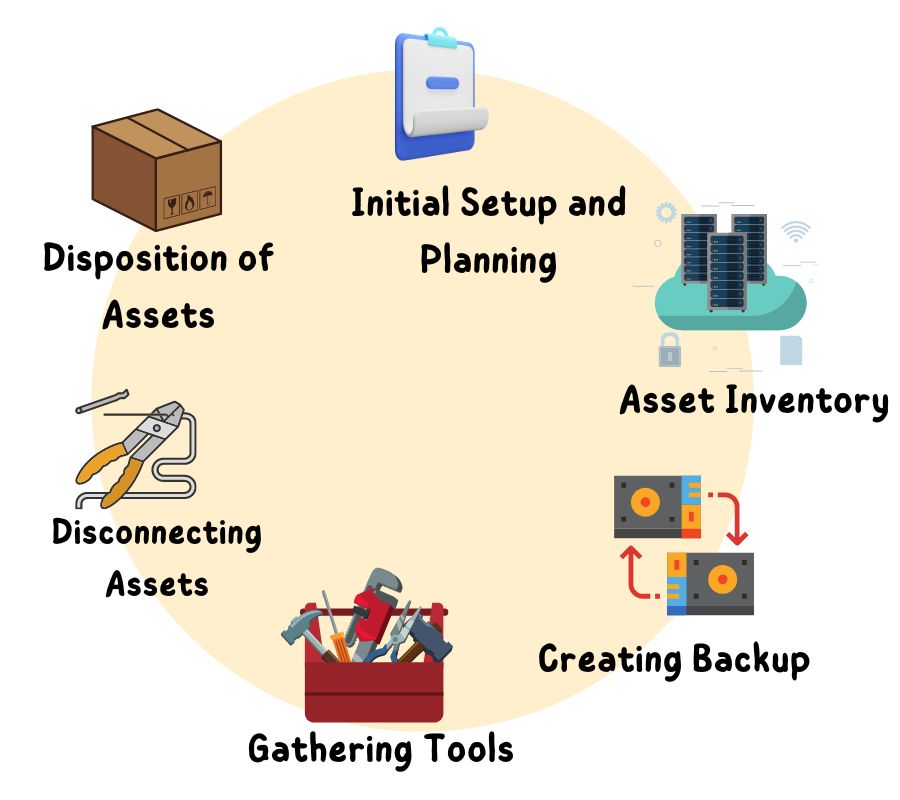
In conclusion, implementing the best practices for server decommissioning is not just about safeguarding data but also about upholding legal standards and environmental responsibility. By following these guidelines, you can navigate the decommissioning process with confidence and integrity.