How to Set Up a DNS Server – Embark on the journey of setting up a DNS server with this comprehensive guide, diving into the intricacies of DNS server setup with ease and clarity.
Discover the importance of DNS servers, the process of configuring DNS zones, securing the server, troubleshooting common issues, and more in this enlightening exploration.
Overview of DNS Server Setup
Setting up a DNS server is crucial for the smooth functioning of a network. It plays a vital role in translating domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites and services easily.
Ensure the smooth operation of your business with The Importance of Server Redundancy. Redundant servers provide a safety net, preventing downtime and ensuring continuous access to your website or online services.
Importance of DNS Server
- Ensures efficient and accurate resolution of domain names to IP addresses.
- Improves network performance by reducing latency in accessing websites.
- Enhances security by providing a centralized point for managing domain name resolution.
Role of a DNS Server
- A DNS server acts as a directory that matches domain names to their corresponding IP addresses.
- It helps in load balancing by distributing traffic across multiple servers using DNS round-robin.
- Facilitates email delivery by resolving domain names to mail server IPs through MX records.
Functionality of a DNS Server
-
Domain Name Resolution:
Converts human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses.
-
Zone Management:
Allows the administrator to control DNS records for specific domains.
-
Cache Management:
Stores recently resolved domain name-to-IP mappings for quicker access.
Setting Up a DNS Server Software
To set up a DNS server, you will need to choose a suitable DNS server software, install it on your system, and configure it according to your requirements.
Make the right choice for your business with guidance on How to Choose the Best Server for Your Business. Selecting the best server tailored to your needs is crucial for optimal performance and scalability.
List of Popular DNS Server Software Options:
- Bind (Berkeley Internet Name Domain): A widely used and highly reliable DNS server software.
- PowerDNS: Offers high performance and flexibility, supporting various backends.
- Unbound: Focuses on security and is known for its speed and efficiency.
- DNSMasq: Lightweight and easy to configure, suitable for small networks.
Steps to Install the Chosen DNS Server Software:
- Download the latest version of the DNS server software from the official website.
- Follow the installation instructions provided for your operating system (Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.).
- Configure the DNS server software settings based on your network requirements and domain setup.
- Start the DNS server service and ensure that it is running correctly.
System Requirements for Running a DNS Server:
It is essential to ensure that your system meets the necessary requirements to run a DNS server smoothly and efficiently.
- Hardware: Sufficient RAM and processing power to handle DNS queries effectively.
- Operating System: Compatible with the DNS server software you choose to install.
- Network Connectivity: Stable internet connection to provide DNS resolution services.
- Firewall Configuration: Properly configure firewall settings to allow DNS traffic.
Configuring DNS Zones: How To Set Up A DNS Server
When setting up a DNS server, configuring DNS zones is a crucial step in managing and resolving domain names to IP addresses. DNS zones are essentially the portions of a domain for which a particular DNS server is responsible. They allow for the organization and delegation of specific parts of a domain, enabling efficient DNS resolution.
Creating DNS Zones
Creating DNS zones involves defining the boundaries of authority for a specific domain within the DNS server. This includes specifying the start of authority (SOA) record, name server (NS) records, and other resource records that provide information about the domain’s DNS settings.
The process typically requires access to the DNS server configuration settings or a dedicated DNS management interface.
- Primary DNS Zone:This type of DNS zone contains the original and authoritative copy of the domain’s DNS records. Changes to the zone’s records are made directly on the primary DNS server.
- Secondary DNS Zone:Secondary DNS zones contain a read-only copy of the primary DNS zone’s records. These zones are used for redundancy and load distribution, providing backup name resolution services.
- Forward Lookup Zone:Forward lookup zones map domain names to IP addresses, allowing DNS resolution from a domain name to an IP address.
- Reverse Lookup Zone:Reverse lookup zones perform the opposite function of forward lookup zones, translating IP addresses to domain names for reverse DNS lookups.
Setting Up Forward and Reverse DNS Lookup
When setting up a DNS server, it is crucial to configure both forward and reverse DNS lookup to ensure smooth and efficient domain name resolution. Forward DNS lookup maps a domain name to an IP address, while reverse DNS lookup does the opposite, mapping an IP address to a domain name.
Embrace the power of technology with The Best Digital Tools for Social Media Growth to elevate your online presence and reach a wider audience. Stay ahead of the game by utilizing these innovative tools for social media success.
Configuring Forward DNS Lookup
Forward DNS lookup is essential for translating domain names to IP addresses. Here are the steps to configure forward DNS lookup:
- Access your DNS server software and locate the forward lookup zone settings.
- Create a new forward lookup zone and enter the domain name for which you want to configure DNS resolution.
- Add the necessary DNS records, such as A records for IPv4 addresses or AAAA records for IPv6 addresses.
- Save the configuration and ensure that the DNS server is running correctly to resolve domain names to IP addresses.
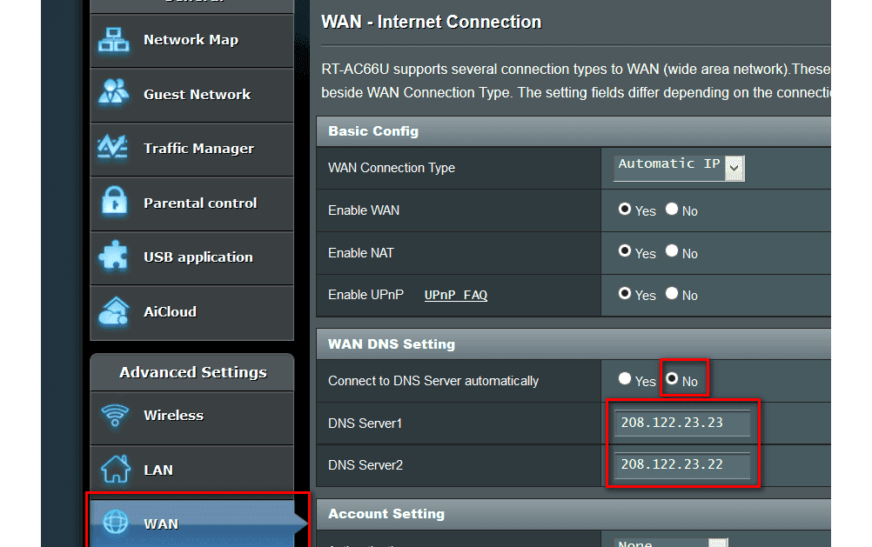
Configuring Reverse DNS Lookup
Reverse DNS lookup is crucial for verifying the authenticity of an IP address by mapping it back to a domain name. Follow these steps to configure reverse DNS lookup:
- Access the DNS server software and locate the reverse lookup zone settings.
- Create a new reverse lookup zone and specify the IP address range for which you want to configure reverse DNS resolution.
- Add PTR (Pointer) records mapping the IP addresses to corresponding domain names.
- Save the configuration and ensure that the reverse DNS lookup is functioning correctly for IP address verification.
Securing the DNS Server
Securing a DNS server is crucial to protect it from potential cyber attacks and ensure the reliability and integrity of your network. By implementing best practices for securing a DNS server, you can prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats that may compromise the functionality of your DNS infrastructure.
Implementing Access Control
One of the fundamental security measures for a DNS server is implementing access control to restrict who can make changes to the server’s configuration and access sensitive information. This can be achieved by:
- Using strong passwords and regularly updating them.
- Enabling multi-factor authentication for additional security layers.
- Restricting access to the DNS server based on IP addresses or network segments.
Monitoring and Logging, How to Set Up a DNS Server
Monitoring and logging activities on the DNS server are essential to detect any suspicious behavior or potential security incidents. By regularly reviewing logs and monitoring network traffic, you can identify and respond to security threats promptly. Key practices include:
- Enabling logging for DNS queries, updates, and zone transfers.
- Setting up alerts for unusual activities or unauthorized access attempts.
- Regularly reviewing logs and investigating any security incidents.
Regular Software Updates
Keeping the DNS server software up to date is critical to address vulnerabilities and security flaws that could be exploited by malicious actors. Regular software updates ensure that you have the latest security patches and enhancements to protect your DNS infrastructure.
This involves:
- Installing security updates and patches released by the software vendor.
- Regularly checking for updates and scheduling maintenance windows for updates.
- Testing updates in a controlled environment before deploying them to production.
Troubleshooting DNS Server Setup
When setting up a DNS server, it is common to encounter issues that may prevent it from functioning correctly. Troubleshooting these problems is essential to ensure the smooth operation of your server.
Common Issues during DNS Server Setup
- Incorrect configuration settings leading to DNS resolution failures.
- Network connectivity issues preventing communication with other DNS servers.
- Firewall restrictions blocking DNS traffic.
- DNS cache poisoning causing incorrect responses to queries.
How to Troubleshoot DNS Configuration Problems
- Verify the DNS server settings to ensure they are accurate and up to date.
- Check network connections to confirm proper communication between servers.
- Review firewall rules to allow DNS traffic to pass through.
- Monitor DNS logs for any error messages or warnings that indicate issues.
Tools and Techniques for Diagnosing DNS Server Issues
- Use command-line tools like nslookup or dig to perform DNS queries and analyze responses.
- Utilize DNS monitoring software to track server performance and detect anomalies.
- Engage in packet capturing to inspect DNS traffic for abnormalities or errors.
- Consider consulting online forums or communities for expert advice on resolving complex DNS issues.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, mastering the art of setting up a DNS server opens up a world of possibilities in the digital realm, empowering you to navigate the complexities of networking with confidence and expertise.