Embark on a journey to discover The Best Practices for Server Patch Management, where wisdom and insights converge to illuminate the path towards enhanced security and operational excellence.
Unveil the strategies and techniques that can revolutionize the way you manage server patches, ensuring a robust and resilient digital infrastructure.
Introduction to Server Patch Management: The Best Practices For Server Patch Management
Server patch management involves the process of applying updates, patches, and fixes to server software to ensure security, stability, and performance.
Implementing effective patch management practices is crucial for maintaining a secure and reliable server environment. Regularly updating servers with the latest patches helps to address vulnerabilities and protect against potential cyber threats.
For startups, finding the best server solutions is essential for scalability and performance. Explore The Best Server Solutions for Startups to discover options that can help your business thrive and grow.
The Importance of Patch Management
- Enhances Security: Patching servers reduces the risk of security breaches and cyber attacks by addressing known vulnerabilities.
- Improves Performance: Updates often include performance enhancements that can optimize server operations and improve efficiency.
- Ensures Compliance: Following patch management best practices helps organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements and industry standards.
Risks of Neglecting Patch Management
-
Data Breaches: Failure to patch servers can leave them vulnerable to exploitation by threat actors, leading to potential data breaches and loss of sensitive information.
When setting up a server, one crucial step is learning how to configure a server firewall. This ensures the security and protection of your data and network. Additionally, for startups, it’s essential to explore the best server solutions that fit your needs and budget.
Stay ahead in the digital age by understanding how to use digital tools to track social media trends for better marketing strategies.
-
Downtime and Disruption: Unpatched servers are more susceptible to crashes, downtime, and performance issues, impacting business operations and productivity.
Tracking social media trends is key to staying ahead in the digital landscape. Learn how to utilize digital tools effectively in How to Use Digital Tools to Track Social Media Trends and elevate your social media strategy.
-
Reputation Damage: Security incidents resulting from unpatched servers can tarnish an organization’s reputation and erode customer trust.
Configuring a server firewall is crucial for protecting your data and network security. By following the steps outlined in How to Configure a Server Firewall , you can ensure that your server is safeguarded against potential threats.
Best Practices for Server Patch Management
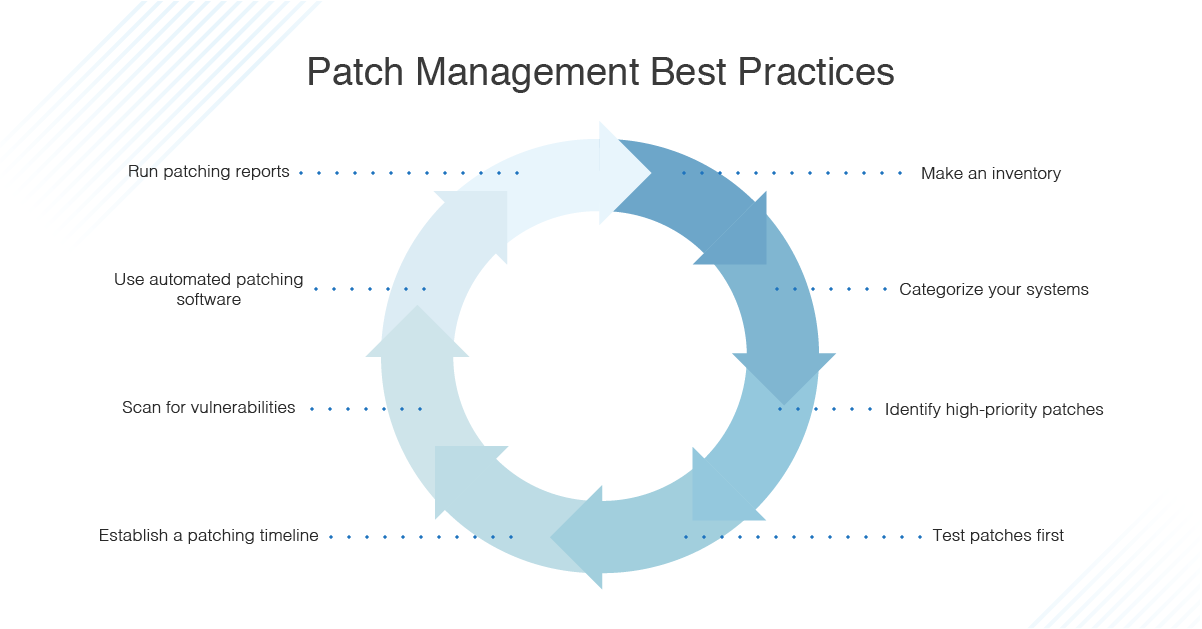
Keeping servers up to date with the latest patches is crucial for maintaining the security and functionality of your systems. Regular updates help to address vulnerabilities and weaknesses in software, reducing the risk of cyber attacks and data breaches.
The Importance of Regular Patch Updates
- Regular patch updates ensure that your servers are protected against the latest security threats and exploits.
- By staying up to date with patches, you can prevent potential downtime and disruptions to your operations.
- Updating patches helps to improve system performance and stability, ensuring a smooth user experience.
Frequency of Patch Updates
- Patch updates are typically released by software vendors on a regular basis, often monthly or even more frequently for critical vulnerabilities.
- It is important to stay informed about the release schedule of patches for your systems and applications to ensure timely updates.
- Regularly checking for updates and applying them promptly is essential to maintain a secure and reliable server environment.
Testing Patches Before Deployment
- Before deploying patches to your production servers, it is important to test them in a controlled environment to ensure compatibility and functionality.
- Testing patches helps to identify any potential conflicts or issues that may arise after deployment, reducing the risk of system failures.
- Having a proper testing process in place allows you to validate the effectiveness of patches and minimize the impact on your production environment.
Automating Patch Management Processes
Automating patch management processes can greatly streamline the task of keeping servers up to date with the latest security patches and updates. By utilizing automation tools, organizations can ensure that patches are applied promptly and consistently across all servers, reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities and downtime.
Benefits of Automating Patch Management
- Improved Efficiency: Automation eliminates the need for manual intervention, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced Security: Automated patch management ensures that critical updates are applied promptly, reducing the window of vulnerability.
- Consistency: Automation helps maintain uniformity in patch deployment, reducing the chances of human error.
- Compliance: Automated patch management can help organizations adhere to regulatory requirements by ensuring that all systems are up to date.
Tools and Software for Automating Patch Updates
- Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM): A popular tool for automating patch management in Windows environments.
- WSUS (Windows Server Update Services): Allows organizations to centrally manage and distribute updates across Windows servers.
- Third-party Patch Management Tools: Solutions like Ivanti, ManageEngine, and SolarWinds Patch Manager offer comprehensive patch automation capabilities.
Improving Efficiency and Security with Automation
Automating patch management processes not only saves time and resources but also enhances security by ensuring timely and consistent patch deployment. By leveraging automation tools, organizations can reduce the risk of security breaches and maintain a strong defense against evolving threats.
Patch Management Strategies for Different Server Types
When it comes to patch management, different server types require specific strategies to ensure optimal security and performance. Let’s explore the patch management approaches for Windows servers, Linux servers, and the best practices for patching physical servers versus virtual servers.
Windows Servers:
- Regularly schedule and automate updates to ensure all critical patches are applied in a timely manner.
- Utilize Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) for centralized patch management and deployment.
- Test patches in a controlled environment before rolling them out to production servers to avoid compatibility issues.
- Implement group policies to enforce patch installation and system reboot policies.
Linux Servers:
- Leverage package managers like YUM or APT to manage patches and updates efficiently.
- Create a patch management schedule to regularly check for updates and apply them promptly.
- Maintain a backup of critical system files before applying patches to mitigate any potential risks.
- Utilize tools like Ansible or Puppet for automated patch management across multiple Linux servers.
Physical Servers vs. Virtual Servers:, The Best Practices for Server Patch Management
- For physical servers, schedule maintenance windows to minimize downtime during patching activities.
- Ensure proper backup and recovery mechanisms are in place before applying patches to physical servers.
- Virtual servers allow for easier snapshotting and rollback capabilities in case of patch-related issues.
- Leverage virtualization management tools to automate patch deployment and ensure consistency across virtual server instances.
Challenges in Server Patch Management
Implementing patch management can come with its own set of challenges that IT professionals need to navigate. From potential downtime during patching to managing updates in complex server environments, there are several obstacles that need to be addressed for effective patch management.
Common Challenges in Implementing Patch Management
- Compatibility issues: Ensuring that patches do not conflict with existing software or applications on the server.
- Time constraints: Finding the right window of time to apply patches without disrupting critical operations.
- Security risks: Vulnerabilities can arise while waiting to apply patches, posing a threat to the server and data.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges
- Regular testing: Conduct thorough testing of patches in a controlled environment before deploying them to production servers.
- Automation: Implement patch management tools that automate the process to reduce downtime and human error.
- Segmented approach: Divide servers into groups based on criticality to stagger patching and minimize potential disruptions.
Tips for Handling Patching in Complex Server Environments
- Create a detailed patch management plan outlining roles, responsibilities, and procedures for patch deployment.
- Utilize virtualization: Use virtual servers to test patches before applying them to physical servers, reducing risks.
- Establish communication channels: Keep stakeholders informed about patching schedules and potential impacts on operations.
Conclusion
As we reach the end of our exploration into The Best Practices for Server Patch Management, remember that proactive patch management is the cornerstone of a secure and efficient server environment. By implementing these practices, you pave the way for a seamless and protected digital ecosystem.