Proxy servers serve as intermediaries between users and the internet, allowing for enhanced privacy, security, and performance. Two common types of proxy servers are HTTP Proxy and SOCKS Proxy. While they both act as intermediaries, they have distinct features and are used in different scenarios. Here’s a breakdown of each type, their uses, and the differences between them.
HTTP Proxy
What is it?
An HTTP Proxy specifically handles HTTP or HTTPS requests between a client (usually a browser) and a web server. It intercepts and forwards these requests and responses, often for purposes like caching, content filtering, and hiding a user’s IP address.
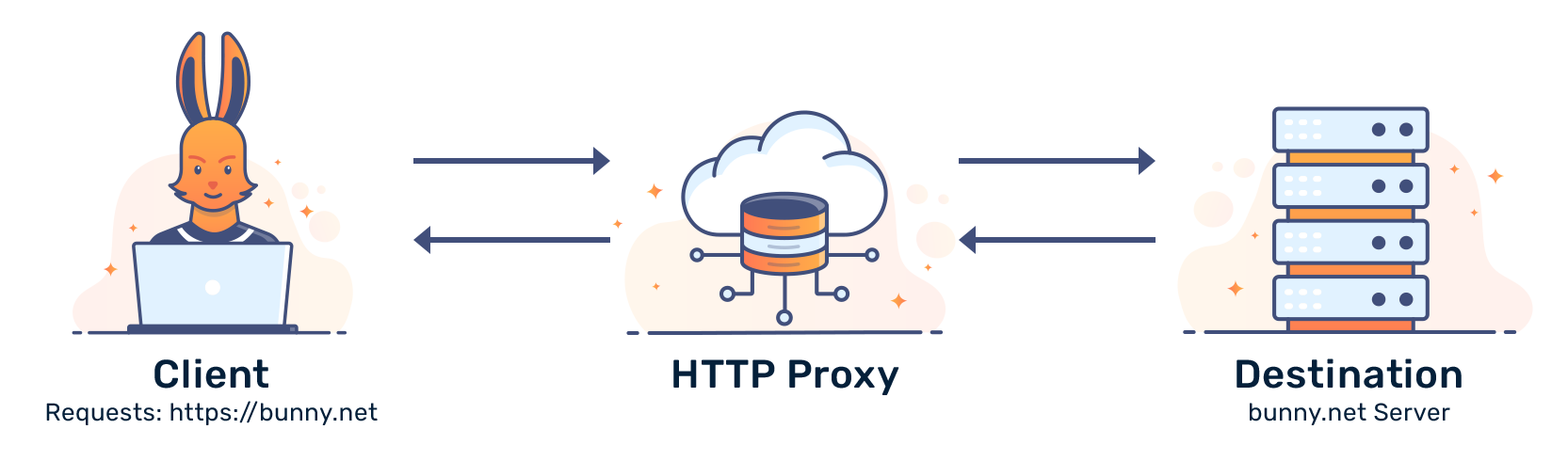
Uses:
- Web Browsing: HTTP proxies are commonly used for everyday browsing to bypass regional restrictions, enhance privacy, or reduce website load times by caching content.
- Content Filtering: Organizations often use HTTP proxies to block access to certain websites, allowing for better control over internet use in offices or schools.
- Caching: An HTTP proxy can cache commonly accessed web pages, speeding up browsing by delivering cached content instead of fetching it from the web server again.
Limitations:
HTTP proxies only handle HTTP and HTTPS traffic, meaning they cannot deal with other types of data, such as FTP, email, or P2P protocols.
SOCKS Proxy: A Flexible and Versatile Internet Tool
What is it?
A SOCKS Proxy (short for Socket Secure) is a more flexible proxy than HTTP proxies. It works with various types of internet traffic like HTTP, FTP, SMTP (email), and more. This makes it a great option for many online activities beyond just web browsing.
Uses:
- Broad Traffic Support: SOCKS proxies can handle different types of internet traffic, including web browsing, emails, and file transfers, giving users more flexibility.
- Bypass Geo-restrictions: SOCKS proxies help you access content that’s blocked in certain regions, making them perfect for streaming or accessing websites from other countries.
- Torrenting: SOCKS5 proxies are popular for downloading and uploading files via P2P networks like BitTorrent. They offer better privacy and security.
- Versatile Access: They support many activities, from web browsing to gaming and file sharing, providing freedom for various online uses.
Limitations:
SOCKS proxies are more flexible but may be slower than HTTP proxies for web browsing since they don’t support caching to speed up web traffic.fer the same caching features that HTTP proxies do, which can optimize web traffic and improve speed.
Key Differences:

| Feature | HTTP Proxy | SOCKS Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Support | Only HTTP/HTTPS | Supports a variety of protocols (HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc.) |
| Use Case | Primarily for web browsing | Suitable for various types of internet traffic, including web browsing, gaming, and P2P |
| Performance | Can cache web content for faster access | More flexible but often slower for browsing due to lack of caching |
| Security | Provides basic anonymity for web traffic | Offers higher anonymity and works with more applications |
| Suitability | Best for browsing websites | Best for users who need to handle different types of traffic, including torrents or streaming |
Both HTTP and SOCKS proxies let users route internet traffic through an intermediary server, but they serve different purposes. HTTP proxies are great for speeding up web browsing with caching, while SOCKS proxies are more flexible, supporting various types of internet traffic. If you need faster web browsing or content filtering, go for HTTP proxies. If you want more freedom for activities like gaming, torrenting, or accessing restricted content, SOCKS proxies are the better choice.